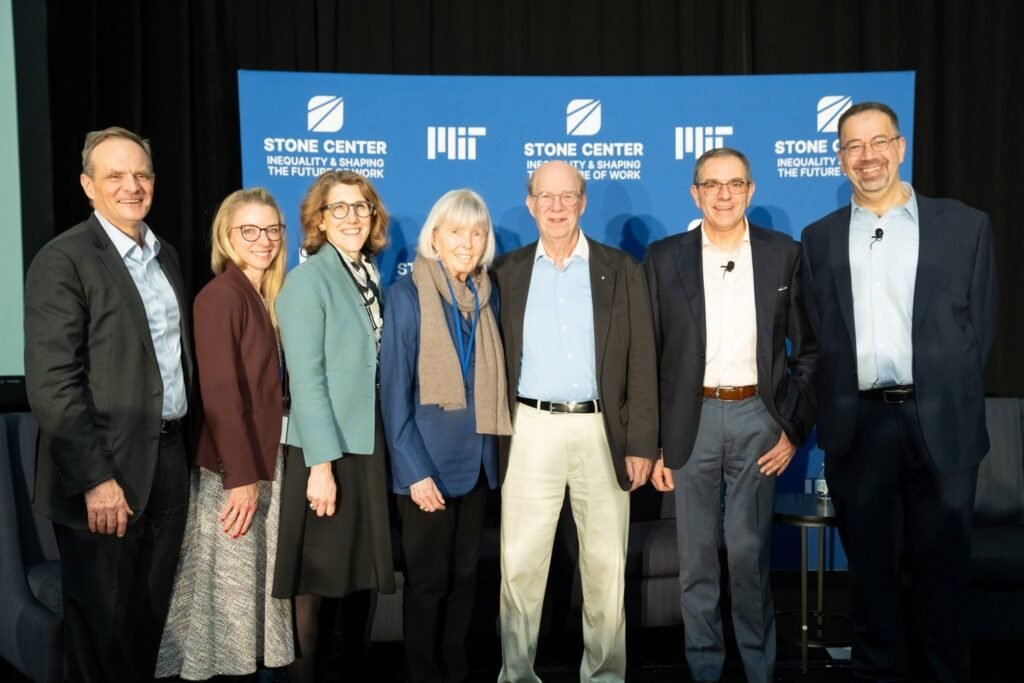
The James M. and Cathleen D. Stone Middle on Inequality and Shaping the Way forward for Work formally launched on Nov. 3, 2025, bringing collectively students, policymakers, and practitioners to discover important questions on financial alternative, expertise, and democracy.
Co-directed by MIT professors Daron Acemoglu, David Autor, and Simon Johnson, the brand new Stone Middle analyzes the forces that contribute to rising revenue and wealth inequality by the erosion of job high quality and labor market alternatives for employees with no school diploma. The middle identifies modern methods to maneuver the economic system onto a extra equitable trajectory.
MIT Provost Anantha Chandrakasan opened the launch occasion by emphasizing the urgency and significance of the middle’s mission. “As synthetic intelligence instruments change into extra highly effective, and as they’re deployed extra broadly,” he stated, “we might want to try to make sure that individuals from all types of backgrounds can discover alternative within the economic system.”
Listed here are among the key takeaways from members within the afternoon’s discussions on wealth inequality, liberalism, and pro-worker AI.
Wealth inequality is pushed by non-public enterprise and public coverage
Owen Zidar of Princeton College pressured that homeowners of companies like automobile dealerships, development corporations, and franchises make up a good portion of the highest 1 %. “For each public firm CEO that will get numerous consideration,” he defined, “there are a thousand non-public enterprise homeowners who’ve a minimum of $25 million in wealth.” These enterprise homeowners have outsized political affect by overrepresentation, lobbying, and donations.
Atif Mian of Princeton College related excessive inequality to the U.S. debt disaster, arguing that large financial savings on the prime aren’t being channeled into productive funding. As an alternative, falling rates of interest push the federal government to run more and more giant fiscal deficits.
To mitigate wealth inequality, audio system highlighted coverage proposals together with rolling again the 20 % deduction for personal enterprise homeowners and rising taxes on wealth.
Nonetheless, insurance policies have to be rigorously designed. Antoinette Schoar of the MIT Sloan College of Administration defined how mortgage subsidy insurance policies after the 2008 monetary disaster truly worsened inequality by disadvantaging poorer potential householders.
Governments should present fundamental public items and financial safety
Marc Dunkelman of the Watson College of Worldwide and Public Affairs at Brown College recognized extreme crimson tape as a key downside for contemporary liberal democracy. “We are able to’t construct high-speed rail. You may’t construct sufficient housing,” he defined. “That spurs peculiar individuals who need authorities to work into the populist camp. We did this to ourselves.”
Josh Cohen of Apple College/the College of California at Berkeley emphasised that liberalism should ship shared prosperity and honest alternatives, not simply defend particular person freedoms. When individuals lack financial safety, they might flip to leaders who abandon liberal ideas altogether.
Liberal democracy must adapt whereas maintaining its core values
Helena Rosenblatt Dhar of the Metropolis College of New York Graduate Middle famous that liberalism and democracy haven’t at all times been allies. Traditionally, “civil equality was essential, however not political equality,” she stated. “Liberals have been very cautious of the lots.”
Audio system emphasised that liberalism’s problem in the present day is sustaining its commitments to limiting authoritarian energy and defending elementary freedoms, whereas addressing its failures.
Doing so, in Dunkelman’s view, would imply working to “get rid of the sowing [of] the seeds of populism by making authorities correctly steadiness particular person rights and the need of the various.”
Individuals-centric politics requires regulating social media
In his keynote on the launch, U.S. Consultant Jake Auchincloss (Massachusetts 4th District) related these notions of presidency effectiveness and public belief to the affect of expertise. He emphasised the necessity to regulate social media platforms.
“For my part, media is upstream of tradition, which is upstream of politics,” he stated. “If we wish a greater tradition, and positively if we wish a greater politics, we’d like a greater media.”
Auchincloss proposed that regulation ought to embrace holding social media corporations responsible for content material and banning focused promoting to minors.
He additionally echoed the urgency and significance of the middle’s analysis agenda, notably to grasp whether or not AI will increase or change labor.
“My bias has at all times been: Know-how creates extra jobs,” he stated. “Perhaps it’s totally different this time. Perhaps I’m unsuitable.”
Augmentation is essential to pro-worker AI — however it might require various AI architectures
Stone Middle co-director Daron Acemoglu argued that increasing what people can do, reasonably than automating their duties, is important for attaining pro-worker AI.
Nonetheless, Acemoglu cautioned that this received’t occur by itself, noting that the enterprise fashions of tech corporations and their give attention to synthetic basic intelligence are usually not aligned with a pro-worker imaginative and prescient for AI. This imaginative and prescient might require public funding in various AI architectures targeted on “domain-specific, dependable information.”
Ethan Mollick of the Wharton College of the College of Pennsylvania famous that AI labs are explicitly making an attempt to “change individuals at the whole lot” and are “completely satisfied that they’ll do that within the very close to time period.”
In the meantime, corporations have “no mannequin for AI adoption,” Mollick defined. “There may be absolute confusion.” Even so, “there’s sufficient cash at stake [that] the machine retains transferring ahead,” underscoring the urgency of intervention.
In a glimpse of what such intervention may appear to be, Zana Buçinca of Microsoft shared analysis findings that accounting for employees’ values and cognition in AI design can allow higher complementarity.
“The influence of AI on human work will not be future,” she emphasised. “It’s design.”